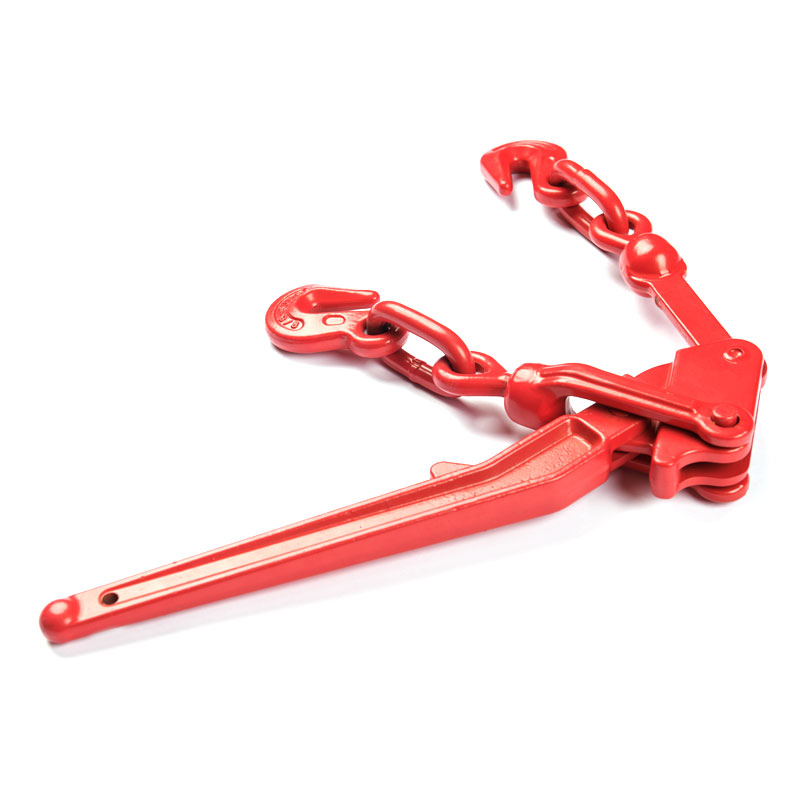

- English
- 简体中文
- Esperanto
- Afrikaans
- Català
- שפה עברית
- Cymraeg
- Galego
- 繁体中文
- Latviešu
- icelandic
- ייִדיש
- беларускі
- Hrvatski
- Kreyòl ayisyen
- Shqiptar
- Malti
- lugha ya Kiswahili
- አማርኛ
- Bosanski
- Frysk
- ភាសាខ្មែរ
- ქართული
- ગુજરાતી
- Hausa
- Кыргыз тили
- ಕನ್ನಡ
- Corsa
- Kurdî
- മലയാളം
- Maori
- Монгол хэл
- Hmong
- IsiXhosa
- Zulu
- Punjabi
- پښتو
- Chichewa
- Samoa
- Sesotho
- සිංහල
- Gàidhlig
- Cebuano
- Somali
- Тоҷикӣ
- O'zbek
- Hawaiian
- سنڌي
- Shinra
- Հայերեն
- Igbo
- Sundanese
- Lëtzebuergesch
- Malagasy
- Yoruba
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик













